Calculating Your Sales Tax Liability in the US: A Step-by-Step Guide for International Businesses
We all know that there will always be one surefire aspect to business – and that’s taxes. But the question then is: are you sure, wherever you operate as a business, that you know your tax liability? It can be a messy matter, especially if you’re an international business operating in the US. And that’s what we’ll be talking about here – this guide is specifically tailored to help foreign businesses understand the essential steps involved in calculating sales tax in the US.
Navigating the US tax system can be particularly challenging for international businesses. The US has a complex and varied approach to sales tax, which differs significantly from the VAT systems common in many other countries. For foreign companies, understanding these nuances is essential to ensure compliance, avoid penalties, and accurately calculate sales tax liabilities. So, whether you’re selling products or services in all, many, or a few states, determining the correct amount of sales tax to collect and remit will ensure you stay on the right side of tax authorities, and compliant as an international business in the US.
Here’s what we’ll be covering:
- Understanding Sales Tax Rates – Explore the variability of sales tax rates across US states and localities with examples.
- Finding the Correct Sales Tax Rate – Learn how to determine the correct sales tax rate by identifying the sale location and checking state and local rates.
- The Sales Tax Calculation Formula – Discover the formula for calculating sales tax and see a practical example applied step-by-step.
- Calculating Sales Price with Tax – Understand the methodology for determining a sales price that includes tax, with a detailed example.
- Backward Sales Tax Calculation – Learn how to calculate the pre-tax sales price from a total price that includes sales tax.
- State and Local Sales Tax Rates, 2024 – Get a breakdown of state and local tax rates for the year 2024.
- Using Sales Tax Calculators – Find out how to leverage automated sales tax calculators for accuracy and compliance, with recommended tools and steps.
Not what you’re looking for? Let’s talk. Reach out to us at info@milesconsultinggroup.com.
1. Understanding Sales Tax Rates
Sales tax rates in the United States vary widely across states and localities. Each state sets its own base sales tax rate, which can be supplemented by local taxes imposed by counties, cities, or special districts. For example, California has a state sales tax rate of 7.25%, but local jurisdictions can add their own rates, resulting in a total rate that can exceed 10% in some areas.
Note: Some states just have a state rate, while others include county or special assessment rates, resulting in a combined overall percentage.
2. Finding the Correct Sales Tax Rate
To determine the correct sales tax rate for your business:
- Identify the location of the sale: This includes where the product is delivered or where the service is performed.
- Check state and local tax rates: Use resources such as state tax authority websites or online databases to find current rates. Just to make things a little easier though, we’ve compiled the latest rates for you in a table a little further on – keep reading.
- Apply the rate to your sale: Ensure that you use the combined state and local rate for the transaction’s location.
3. The Sales Tax Calculation Formula
Calculating sales tax involves a straightforward formula:
Sales Tax=Sales Price×Sales Tax Rate
Step-by-Step Guide
- Determine the Sales Price: The price of the product or service before tax.
- Identify the Sales Tax Rate: Use the correct combined state and local rate.
- Multiply the Sales Price by the Sales Tax Rate: This gives you the amount of sales tax to collect.
- Add the Sales Tax to the Sales Price: This gives you the total price that the customer pays.
4. Calculating Sales Price with Tax
Sometimes, you need to determine the sales price inclusive of tax, especially in retail settings where prices are displayed with tax included.
Note: In California, certain disclaimers like ‘we pay your sales tax’ mean the seller is choosing not to collect sales tax at the point of sale, but the tax is still due, representing a liability that needs to be considered.
Methodology
To find the total sales price with tax included:
Total Price=Sales Price×(1+Sales Tax Rate)
Example:
With a sales price of $100 and a tax rate of 8.875%:
Total Price=$100×(1+0.08875)=$100×1.08875=$108.88
5. Backward Sales Tax Calculation
In some scenarios, you might need to work backwards from a total price that includes sales tax to determine the original sales price and the amount of tax included.
To find the pre-tax sales price:
Example
If the total price paid is $108.88 and the sales tax rate is 8.875%:
These formulae and methodologies can be applied universally, regardless of the sales tax rate or the initial sales price, ensuring accurate calculations for both inclusive and exclusive tax scenarios.
6. State and Local Sales Tax Rates, 2024
A breakdown of average state, local and combined tax rates.
Remember, though, these percentages are subject to change on a regular basis. Always be tax-savvy – check these rates regularly to avoid unpleasant surprises at filing time.
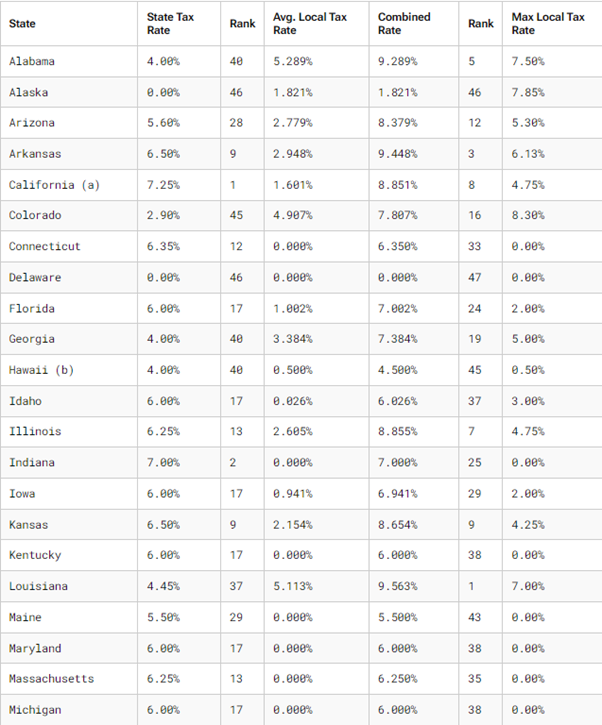
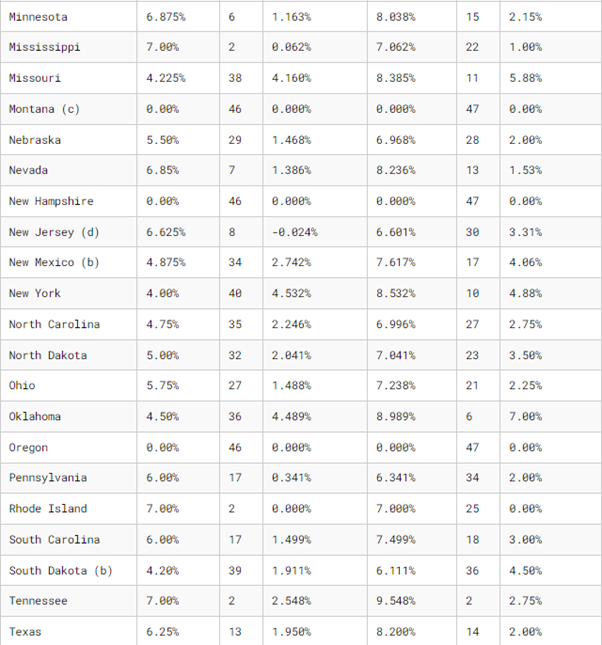
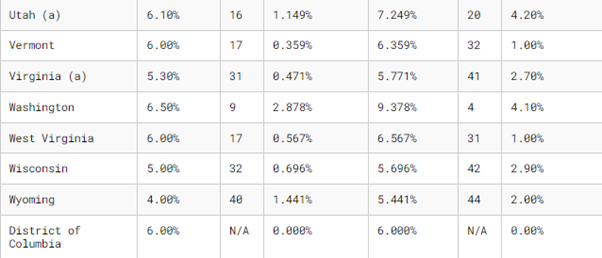
Note: City, county and municipal rates vary. Local rates are weighted by population to compute an average local tax rate.
(a) Three states levy mandatory, statewide, local add-on sales taxes at the state level: California (1.25%), Utah (1.25%), and Virginia (1%). We include these in their state sales tax.
(b) The sales taxes in Hawaii, New Mexico, and South Dakota have broad bases that include many business-to-business services.
(c) Special taxes in local resort areas are not counted here.
(d) Salem County, N.J., is not subject to the statewide sales tax rate and collects a local rate of 3.3125%. New Jersey’s local score is represented as a negative.
Sources: Sales Tax Clearinghouse; Tax Foundation calculations; State Revenue Department websites.
Source: Tax Foundation
7. Using Sales Tax Calculators
Automated tools can significantly simplify the task of calculating sales tax, especially for businesses operating in multiple jurisdictions. These tools ensure compliance with varying tax rates and regulations across different locations. (We’ve been around long enough that some of our clients have done calculations manually…but those days are pretty far behind us!)
While automated sales tax calculators, such as those provided by Avalara, QuickBooks, and TaxJar, and through sales portals like Shopify offer robust solutions, human oversight is essential for accuracy. This is necessary to account for potential changes in tax laws and local regulations that automated systems might not immediately reflect. The human touch is vital, and that’s where Miles Consulting can help.
How to Use Sales Tax Calculators
- Choose a Reliable Calculator:
- Look for calculators provided by reputable sources such as tax authority websites, accounting software, and well-known online resources. It’s important to choose tools that are regularly updated to reflect the latest tax rates and rules.
- Example calculators include those offered by state departments of revenue, accounting software like QuickBooks, and dedicated tax services like Avalara and TaxJar.
- Input Sales Data:
- Enter the sales price of the product or service.
- Provide the necessary location details where the sale occurs (i.e.; if brick and mortar – then at the store; if in e-commerce, the “ship to” address). This includes the state, county, and city, as local tax rates can vary significantly.
- Verify the Results:
- After entering the data, review the results to ensure the calculator has applied the correct combined state and local tax rates.
- Cross-reference with official tax rate information from state or local tax authority websites to confirm accuracy.
By leveraging these tools, businesses can streamline their sales tax calculation processes, reduce errors, and ensure compliance with tax regulations across multiple jurisdictions. However, always remember to periodically verify the accuracy of these tools and stay informed about changes in tax laws that may affect your business.
And we’ve said it before, but we’ll say it again, it’s always better to first consult with a human. Come to Miles Consulting Group – book a consultation, drop us a line, or send us an email at info@milesconsultinggroup.com.